Open Visual studio and create a new Project. Search for Python in the templates.
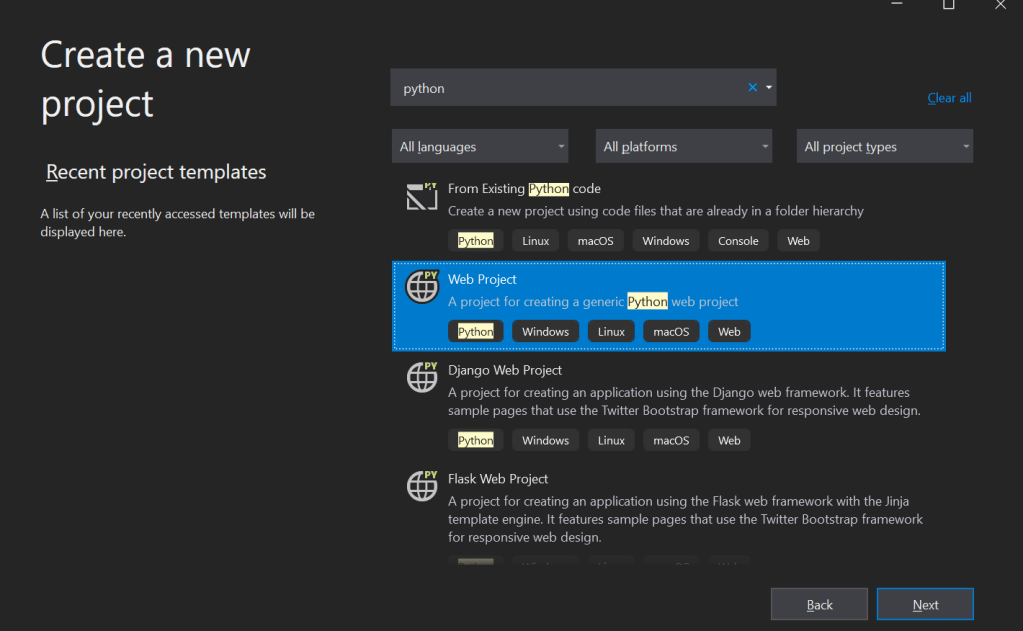
Select Python web project and click on “Next“. Then, click “Create“

This creates a new Python project and can be viewed under “Solution Explorer“.
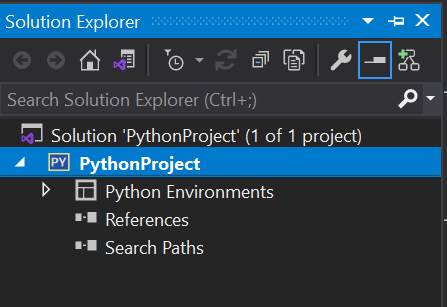
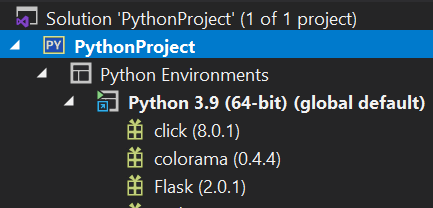
Let’s install a python library called Flask. Expand Python Environments, you should be able to see the version of the Python that is installed.
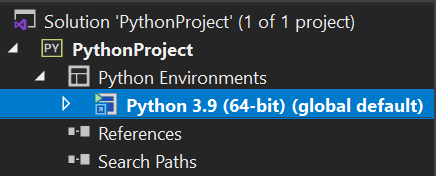
Right click on the python version and click on Manage Python Packages.
Search for “Flask” and click on “Run command PIP install Flask“.
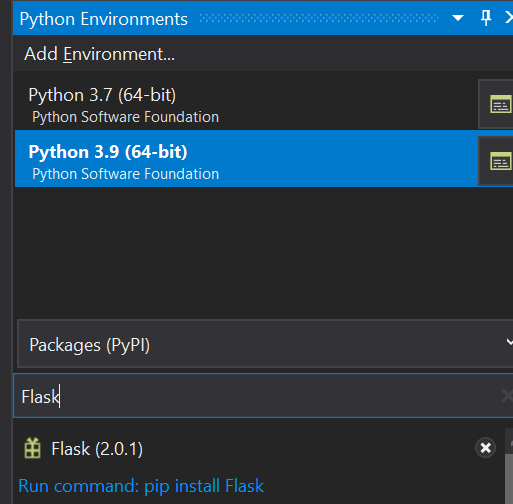
Once, it is installed, it will show up under the solution explorer -> Under Python environments.
Now, let’s add a new Python code file.
Right click on the Project name, in our case “PythonProject” under Solution explorer. Select Add -> New Item.
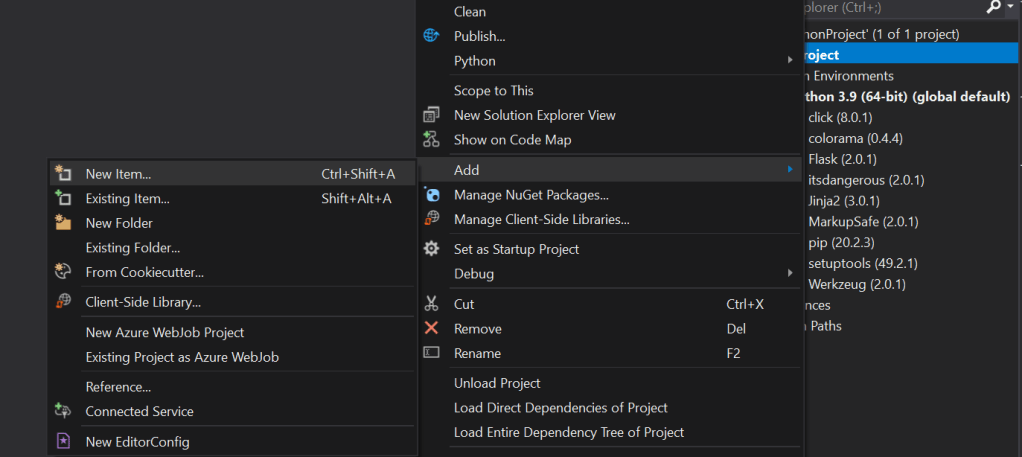
Select Empty Python File, change the name of the file to app.py. Click Add.

Once done, open the app.py file and add the code as below.
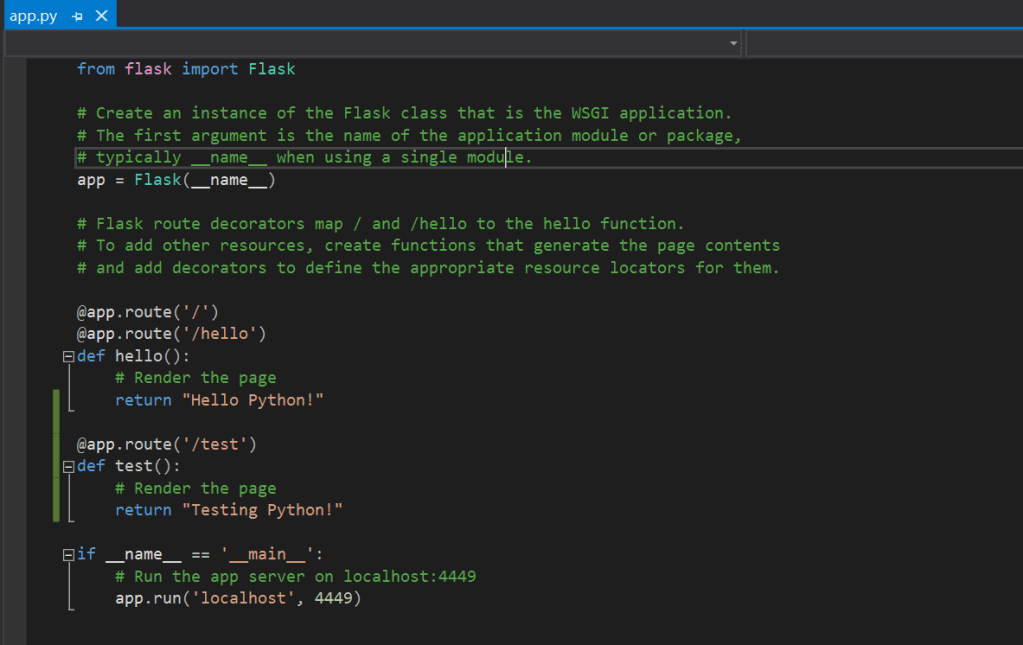
This code creates an app that has two different methods called hello() and test().
There is a route that is defined on top of each methods.
The last if block says that the app should run in the localhost with port number as 4449.
Let’s run this code. Hit the debug button. It should open the web browser with this url – https://localhost:4449.
You should see the output like below:
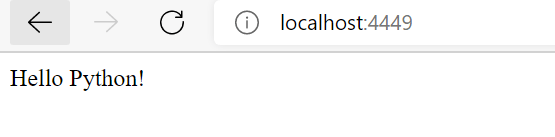
This is because there is one route defined for the app in the code.

This means that whenever there is just the url or it is routed with /hello, it should return “Hello Python“.
Now, let’s change the url to https://localhost:4449/hello. It will render the same output.
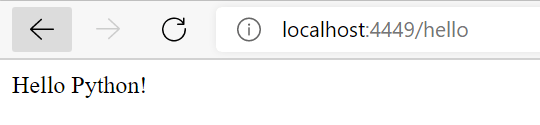
There is another route defined for the app in the code,

If we change the url now to https://localhost:4449/test, it should return “Testing Python!“
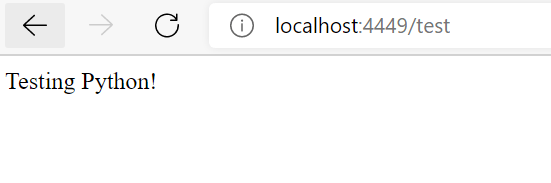
Likewise, we can create applications to render differently on different routes.
Let’s see some more advanced applications in the next post!