Lambda functions are small and anonymous functions.
Lambda function can take ‘n‘ number of arguments, but will have only one expression.
To create a Lambda function in Python, we need use Lambda keyword.
Let’s see with an example. If we assign a function to a variable, it becomes an anonymous function and thus a lambda function.
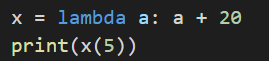
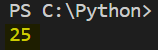
The output of the above statement is:
Here, we have a lambda function which takes variable ‘a’ and adds that variable ‘a’ with 20.
Hence, if we call x(5) -> The lambda function executes and it adds 20 to 5 and hence, the output 25.
Now, let’s try by wrapping the lambda function within a function.
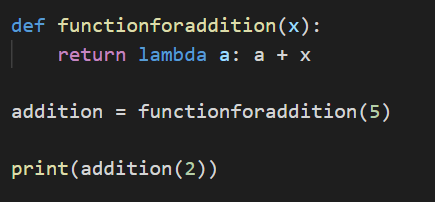
In the above example, functionforaddition(x) is a function that has a lambda function that add the value of x with a. x is the variable that is passed via functionforaddition().
In the second line, we are passing 5 in the functionforaddition(x) and this function we are assigning it to a variable called as addition.
Please note that variable addition is assigned with a function. Usually, we assign a variable with any value, but, here it is assigned with function.
We are calling addition function in the last statement by passing 2 as a parameter.
So, 2 will be replaced with variable ‘a’ and 5 will be replaced with variable ‘x‘.
Hence, the output will be as shown below:
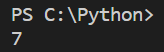
It is adding 2 and 5 and it is displaying the addition of 5 and 2 i.e., 7.
Assigning functions to variable, makes it anonymous, hence, lambda function.