Functions are logical grouping of code statements that collectively performs a specific operation or a specific requirement.
Example: If I am building a calculator, a calculator can perform various mathematical operations like addition, subtraction, division, etc.
I can create one function for addition, one function for subtraction, one function for division, and so on.
Let’s now again further dig down to one function, addition.
What are minimum requirements to perform addition, 2 NUMBERS. We can perform addition only if we have 2 NUMBERS with us. These 2 numbers are called as input parameters or arguments.
When I pass two numbers to addition function, the addition operation can be performed.
During this operation i.e., during the addition of 2 numbers, what is the output or the end result?
1 NUMBER which is the addition of 2 NUMBERS.
Therefore, the 1 NUMBER which is the result of addition of 2 NUMBERS is called the output of the function.
So, we need to pass the input to the function i.e., called as parameters or arguments.
The output that we get after performing an operation within the function can be fetch using the return type.
Let’s understand better with an example:
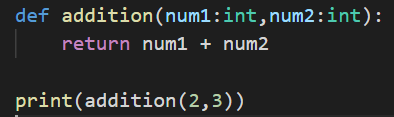
In Python, functions are created using def keyword. In the above code, I have created a function called addition.
addition function takes two parameters, i.e., num1 and num2.
The second statement is the actual addition it is performing, it is returning the value after adding num1 and num2.
Important point to note is: functions code (i.e., addition function here) will not be executed unless or until it is called.
So, what does it mean calling a function.
Let me explain with an example:
Assume that we have only this code,
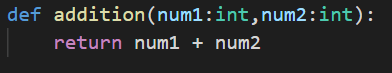
This is again a addition function which takes two numbers as parameters and performs addition operation and return one value.
When we have only this code and try to execute this, we will not see any result.
Why? Because we have not called this function.
Calling a function is invoking a function to execute by providing the required input parameters or arguments values.
In the above code, we don’t know what is the value of num1 and what is the value of num2.
Hence, we will not get any result.
However, if we pass values to these function by calling addition, it will return a value.
Observe this code carefully. We have a function definition addition that is taking two parameters and returning the addition of two parameters that is passed to the function.

In the last line, addition(2,3) -> what is this statment used for?
This is used to call the definition of the addition function by passing two values, i.e., for num1 = 2 and num2 = 3.
return num1 + num2 will be replaced by return 2 + 3 during the execution of the function.
However, even now we will not see any output. Why? Because, we aren’t printing the value of the addition function.
Now, let’s call a function inside a print statement so that the value that is returned from the function can be printed.
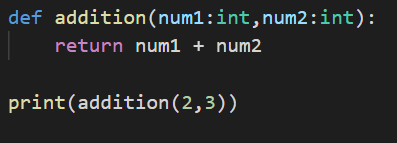
Now let’s see what would be the output:

Yeah. The addition of 2 and 3 is 5. Hence, we got the output as 5.
Now, try similar way for subtraction, multiplication, division, etc until I return to you with one more advanced post on FUNCTIONS.
Please comment or provide your feedback on the blog. Thanks. 🙂