List is a collection which contains objects or items that can be changed and ordered.
Note: List can allow duplicate members.
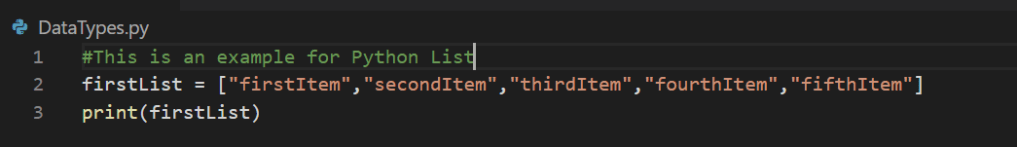
Below is the sample code which creates the list name “firstList” and displays the list.
In Python, lists are written inside a square bracket.
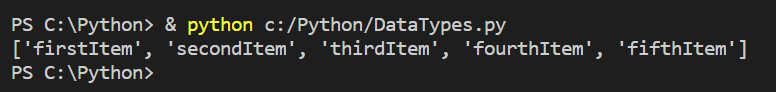
When we print the list, we get the below output:
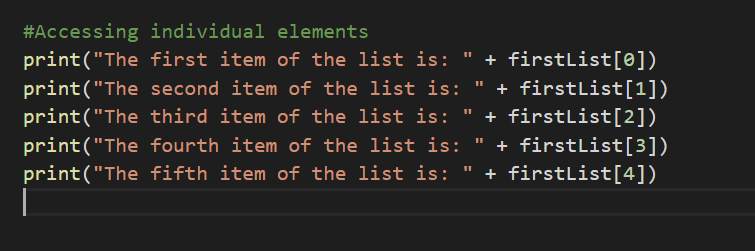
To access individual items, we use indexes. Index starts with zero. First Item is always accessed from 0.
The items of “firstList” can be accessed as shown below.
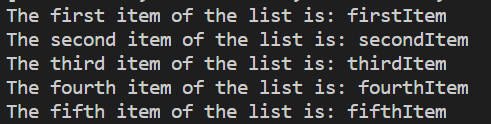
Output of the above code is:
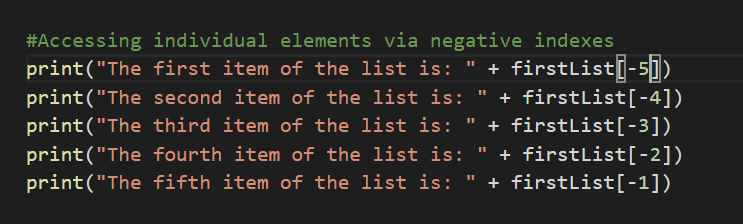
Negative Indexes
This is an unique concept. Can the items be accessed via negative indexes?
Yes. It can be accessed via negative indexes. Negative Index starts from -1. -1 displays last item. -2 displays second last item.
Likewise, more the negative value the corresponding items will be displayed.
Example:
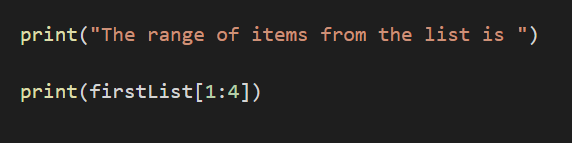
Range
The items in the list can be retrieved based on the ranges.
Example:
Output:
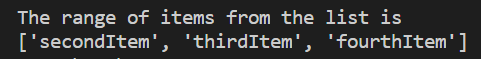
Please note that range will return the items mentioned between the first number and the second number.
In the above example, it will display items from the range of 1 till 4th Item. Here, indexes starts with zero.
Hence, [‘secondItem’,’thirdItem’,’fourthItem’] are displayed however the last item i.e., the item in the 4th index will not be displayed.
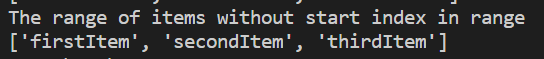
Range will still work if we give just the start item index or the last item index.
Example:

Output:
This will display all the items from the start index i.e., 0 index till 3rd index.
Example:
Similarly, let’s see what happens if the last index is not mentioned.
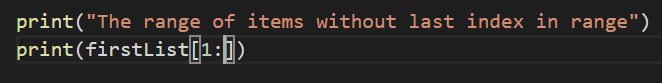
Output:
