Datatypes are common concepts across every language. The data that is stored in a variable determines the data types.
For Example: a variable that stores a text has string as a data type, similarly, variable storing number has int, float or complex as data type depending on the complexity of the number.
Let’s understand few data types here:
Let’s create a new file DataTypes.py file.
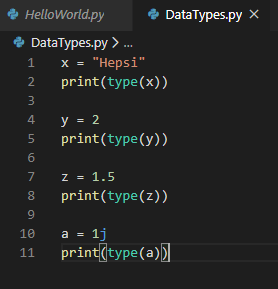
In Line number 1, we have created a variable ‘x‘ which is assigned with value “Hepsi” which is a string.
The datatypes of variable can be known by using type() function.
In Line number 2, we are printing the type of ‘x‘ variable using type() function which takes one variable as the argument.
Similarly, in Line number 4, we have created a variable ‘y’ which is assigned with value 2 which is a number or integer.
In Line number 5, we are print the type of ‘y’ variable using type() function which takes one variable as the argument.
Similarly, in Line number 7, we have created a variable ‘z’ which is assigned with value 1.5 which is a floating number.
In Line number 8, we are print the type of ‘z‘ variable using type() function which takes one variable as the argument.
Similarly, in Line number 10, we have created a variable ‘a’ which is assigned with value 1j which is a complex number.
In Line number 11, we are print the type of ‘a‘ variable using type() function which takes one variable as the argument.
Let’s see what is the output by hitting the run button:
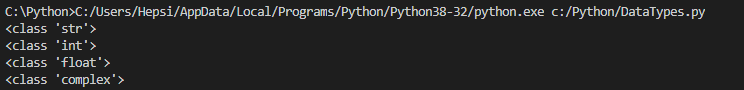
The output clearly shows that we have created a string variable i.e., x , integer variable i.e., y , float variable i.e., z and a complex variable i.e., a.
Before proceeding further, let’s see what is a complex number in the next post.