Variable creation in Python is very much similar to the other programming languages. However, there are few notable differences.
- Variables are created only when it is assigned with a value. There is no concept of declaration.
- Variables type are determined only when it is assigned with a value. Type is optional while creating variables.
- Types can be changed after assigning the value for the variables by assigning it with the data of different type.
Below are the rules that has to be followed while creating variables which is very much similar to the rules that is followed in another programming languages.
- A variable name must start with a letter or the underscore character.
- A variable name cannot start with a number
- A variable name can only contain alpha-numeric characters and underscores (A-z, 0-9, and _ )
- Variable names are case-sensitive (name, Name and NAME are three different variables)
Let’s start by creating few variables.
Create a new file and name it as “variables.py“
Add the code as shown and click the “run” button.
Code:

Output:

We have created a variable named “x” and we are printing the variable “x“.
As mentioned earlier, types of a variable can be changed after assigning the value with the data of different type
Let’s understand it with an example by reusing the same file created earlier.
Code:
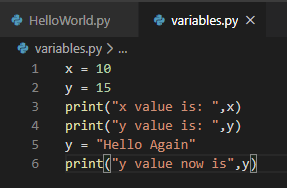
A variable named “y” is created and assigned with a value of 15 which is an integer.
In the line number 5, again the same variable “y” is assigned with a value of “Hello Again” which is a string.
This will not throw any error during compile time nor run time.
Output:
